Info
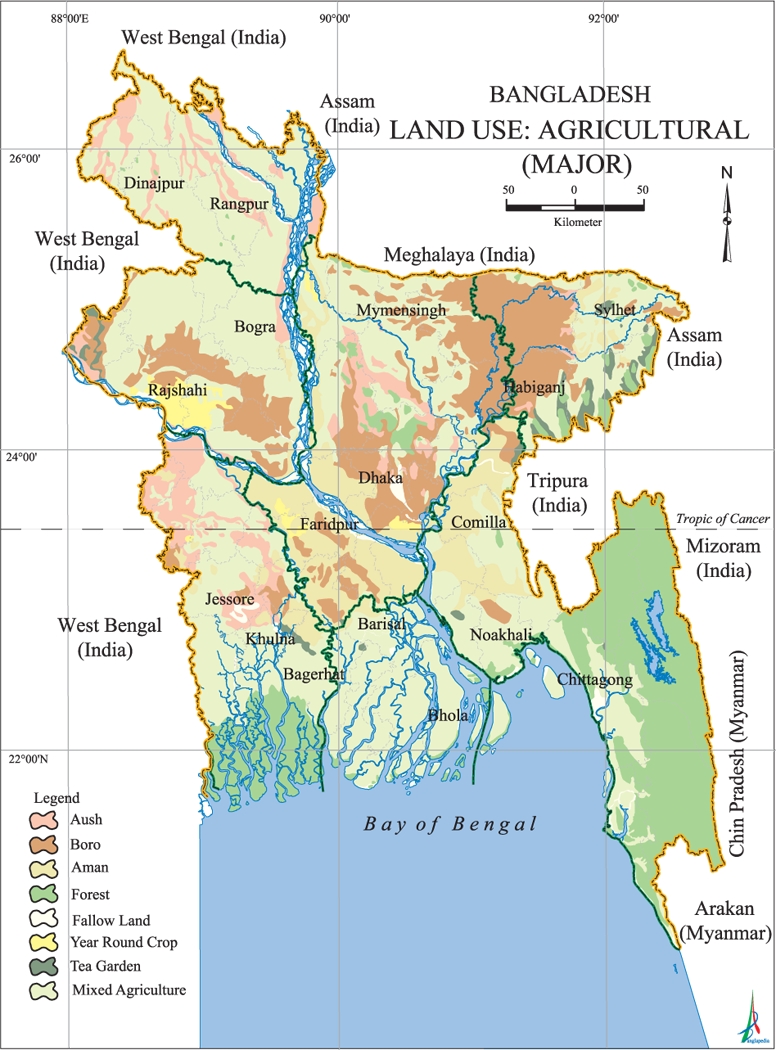
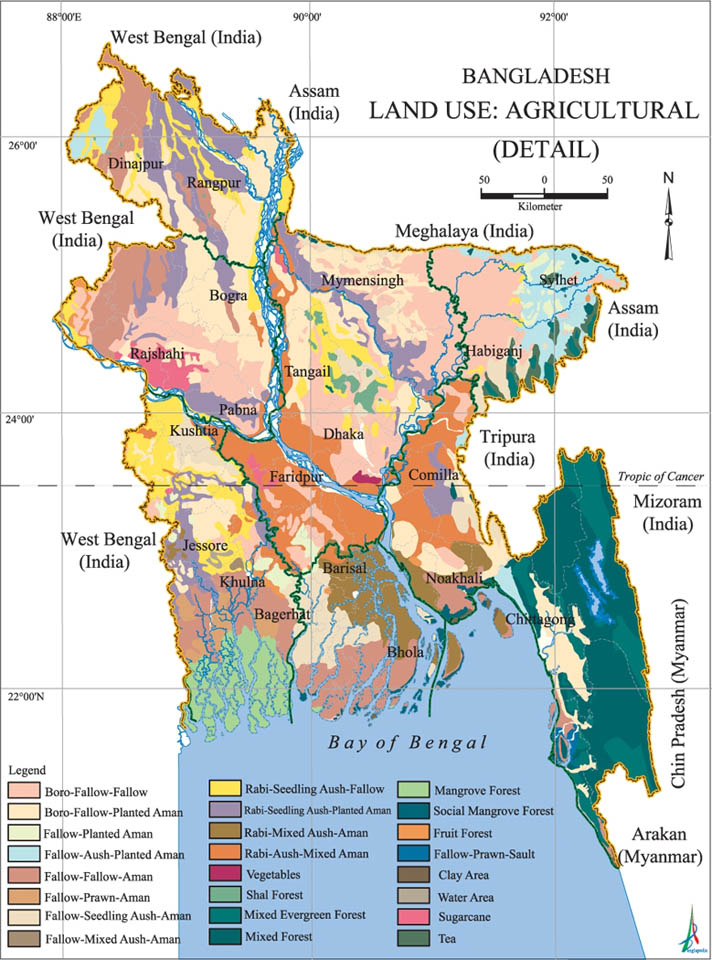
Landuse human activities that are directly related to land, making use of its resources or having an impact upon it. Land cover is the physical attributes of the land, while landuse is a pattern of human activities undertaken within a socio-economic context. Natural land cover is changed by use of man in meeting cultivation, homestead or other demands.
Physiographically Bangladesh may be divided into three major units: hills of the north, northeast and southeast covering about 12 percent of the total area; Pleistocene terraces stretching over only 8 percent area and floodplains accounting for 80 percent of the total area. Of the three determinants, land levels in relation to flood depth are of major importance for landuse. Even occupation types in the rural areas are dependent on flooding characteristics - depth, duration and timing. There are regional variations in the distribution of different land types and landuse pattern.
Landuse pattern in Bangladesh is determined by physiography, climate and land levels in relation to flooding. In this context land includes all land and water within the national boundaries of the country. Water bodies within land areas are therefore considered to be a part of land. The use of land is of paramount importance in a country which is thickly populated and still very reliant on primary production.
Land and water are the two major natural resources of Bangladesh. The total area of Bangladesh is 147,570 sq km of which 9,734 sq km is under inland waterbodies (river, beels, etc), homesteads cover 11,227 sq km, urban fabric covers 950 sq km and forests 2,154 sq km. This account includes the shallow estuarine water surface between the offshore islands in the delta.